Gov. J.B. Pritzker is making extraordinary claims about his $3.4 billion income tax hike. Among them, that it will fill Illinois’ deficit “hole” and bring financial stability to the state.
But the scale of Illinois’ fiscal problems demands an entirely different solution – one that doesn’t force taxpayers and businesses to pour billions of dollars more into a broken system.
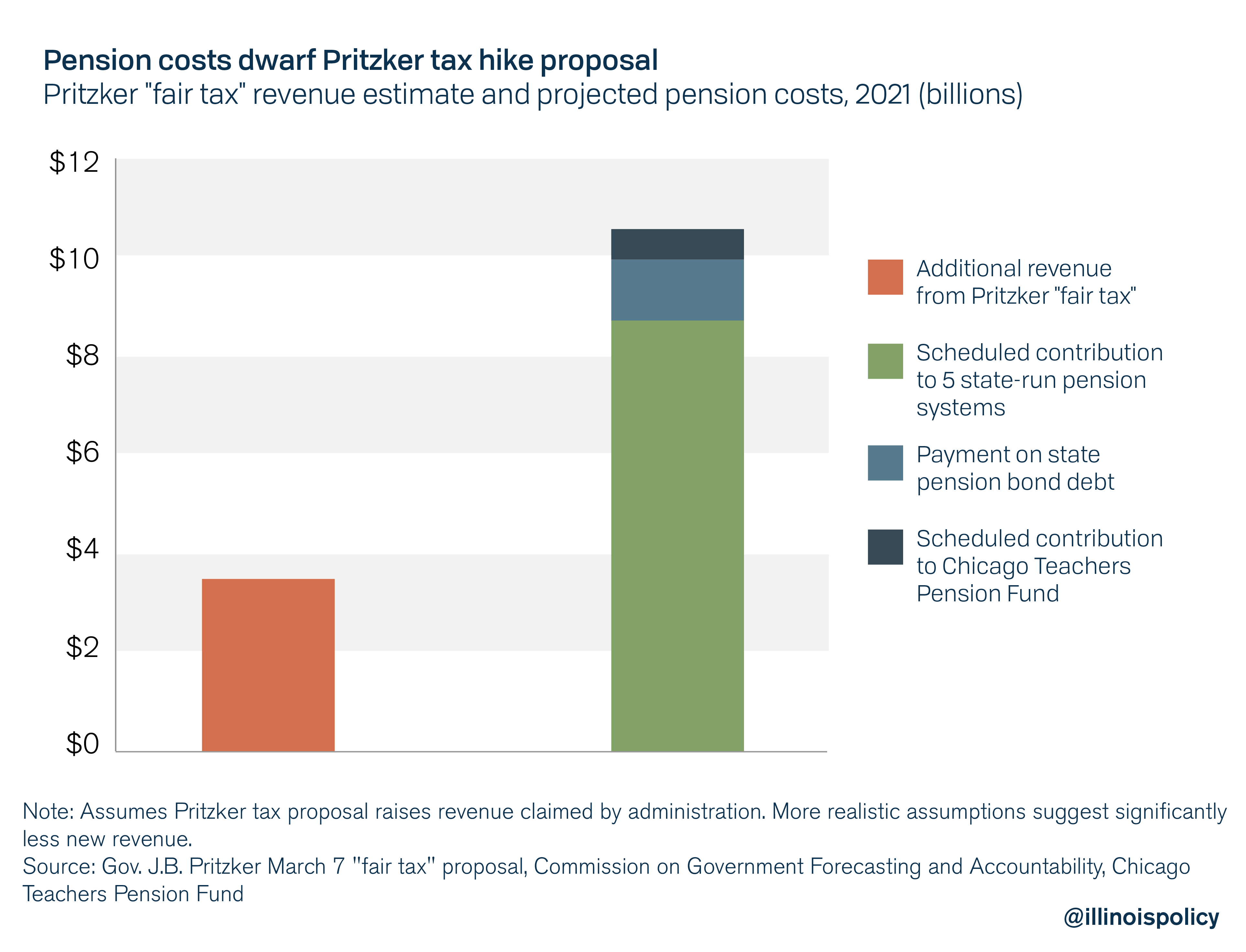
Pritzker’s estimated new revenue would be enough to fund the equivalent of 118 days of state pension costs – less than four months.
If approved by the Illinois General Assembly and voters at the ballot box, Pritzker’s tax plan would be implemented in 2021 at the earliest. Pritzker assumes his plan will generate $3.4 billion that year, a gross overestimation when compared against the state’s historic income growth and national economic trends. But even assuming his plan raises that much, it will be dwarfed by the scope of Illinois’ pension problem.
In 2021, Illinois is scheduled to contribute $9.55 billion to the five state-run pension systems, $250 million to the Chicago Teachers Pension Fund and $713 million in payments on the state’s pension bond debt. That means total pension costs will be $10.51 billion, or more than 27 percent of the state’s expected general revenues.
If Pritzker succeeds in passing a graduated income tax, Illinois’ growing pension costs will ultimately force lawmakers to call for tax hikes on the state’s middle class.
Fixing the pension problem
Illinois’ pension crisis is often reduced to talking points about how the system was either underfunded or overpromised. In reality, one follows from the other.
According to Wirepoints, total pension liabilities, or the present value of current and future promised benefits, have grown 4.5 times faster than Illinoisans’ personal income and six times faster than state revenues since 1987. Underfunding is a result of the fact that required payments were unrealistic to begin with – overpromised. A back loaded funding ramp signed into law by former Gov. Jim Edgar significantly worsened the problem.
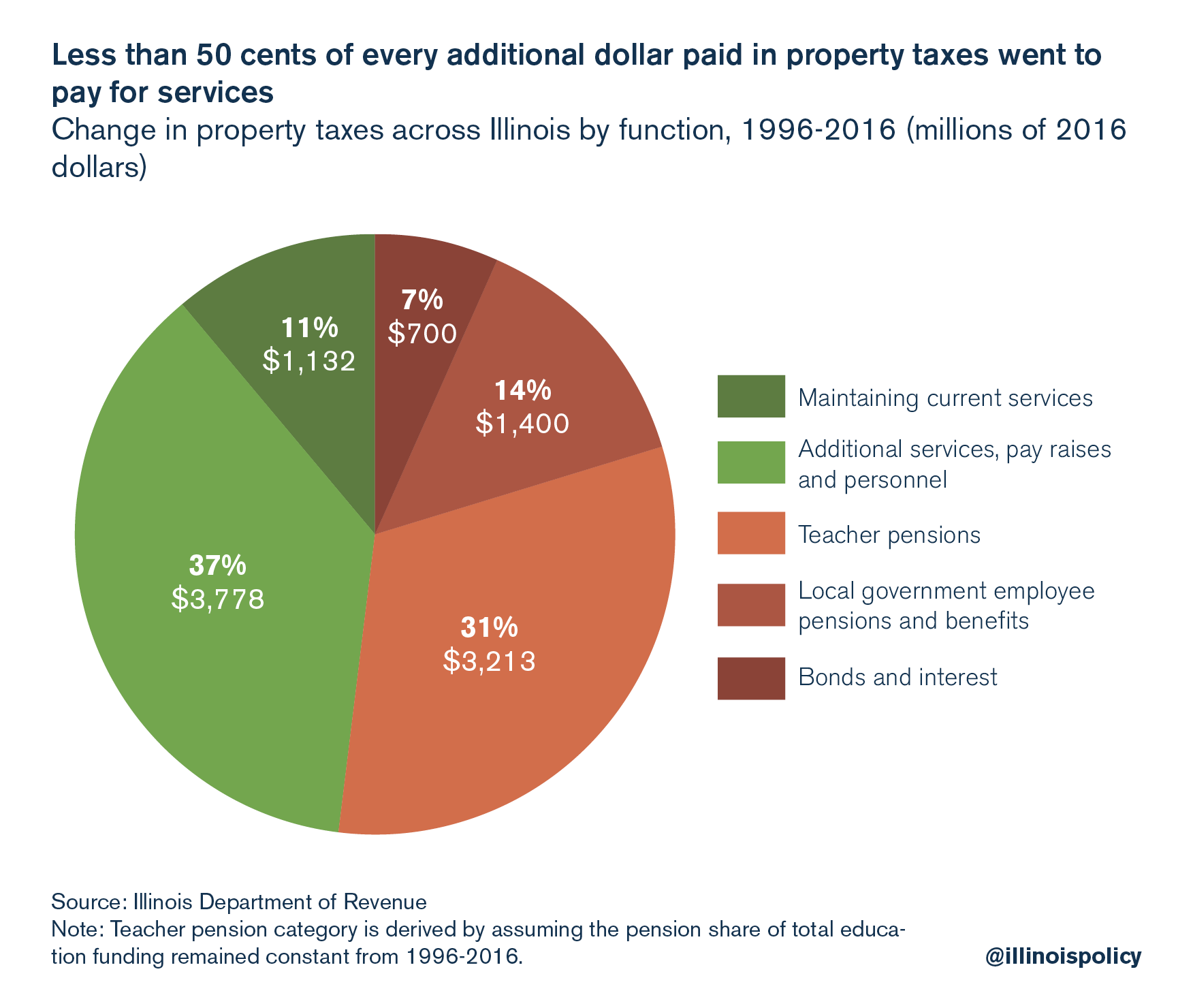
Without reform, pensions will continue to drive up local property tax bills, as well. From 1996 to 2016, increasing pension costs and debt payments accounted for more than half of the growth in residents’ property tax bills, bringing Illinois property tax burdens from around the national average to among the highest of any state.
Instead of devoting enormous political resources to scrap the Illinois Constitution’s flat income tax protection, Pritzker should set his sights on the state’s single largest cost-driver – the constitutional pension clause preventing bipartisan reform to protect the solvency of the state’s retirement funds.
House Joint Resolution Constitutional Amendment 21 and Senate Joint Resolution Constitutional Amendment 9 would do just that. The amendments would protect all pension benefits already earned, meaning the state could keep its promises to current employees and retirees. But it would allow for changes in the growth of future benefits, including provisions such as automatic 3 percent raises in pension benefits for life.
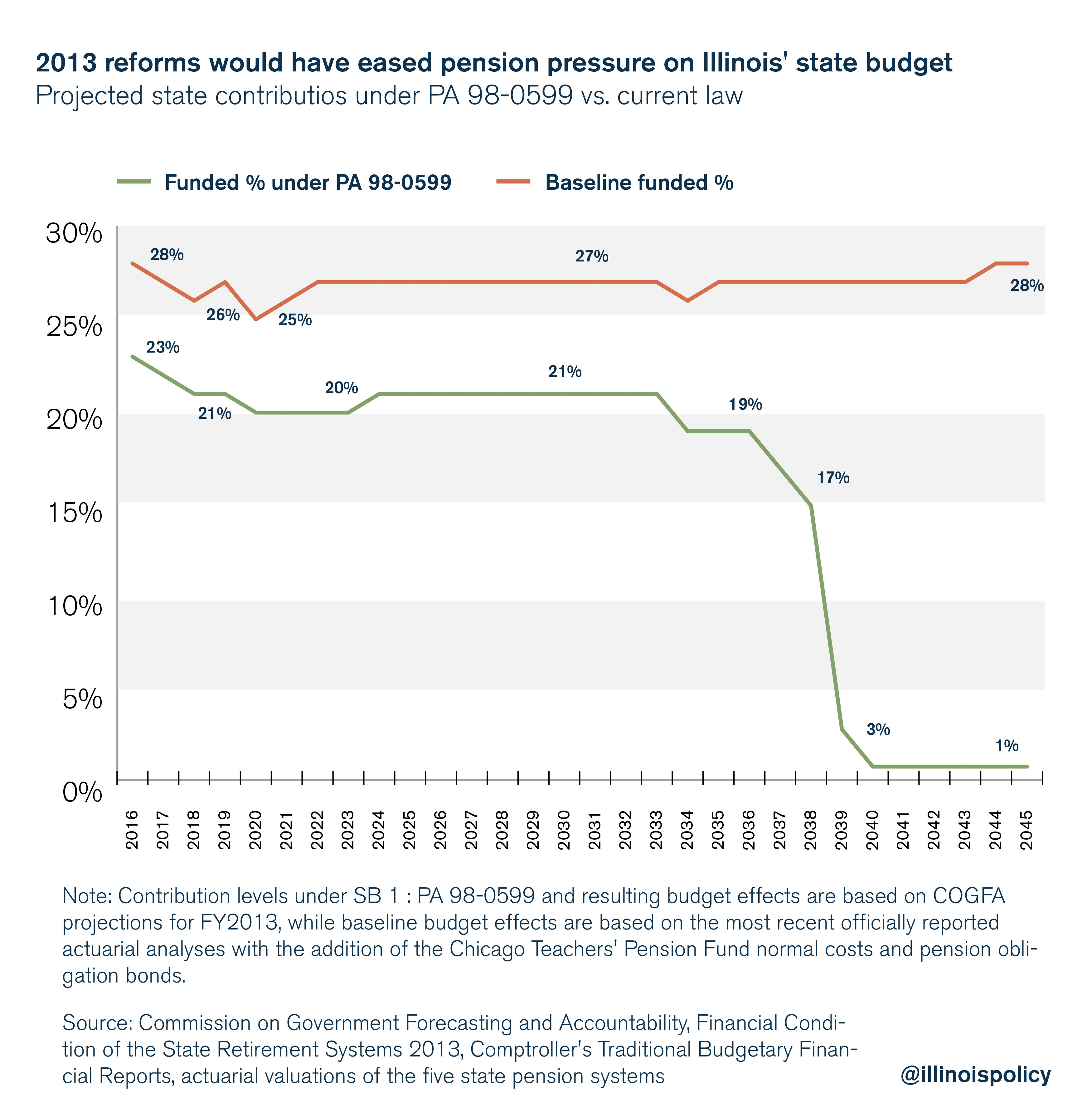
Moving to true cost-of-living adjustments, by tying post-retirement benefit increases to some measure of inflation, was part of a reform effort that passed Illinois’ General Assembly in 2013 but was struck down by the state’s Supreme Court in 2015. Had the reforms survived, they would have reduced the state’s 2016 pension contribution by $1.2 billion and put the state on a path toward a sustainable and affordable pension system.
If state lawmakers fail to tackle the pension problem, Illinois taxpayers will continue to pay more and get less from their state and local governments.